Electrification and Hybrid Propulsion: Transforming Sustainable Shipping with Practical Applications for Short-Voyage Vessels
Electrification and Hybrid Propulsion: Transforming Sustainable Shipping with Practical Applications for Short-Voyage Vessels
The global shipping industry is charting a new course towards sustainability, driven by electrification and hybrid propulsion technologies. By combining electric power with traditional propulsion systems, the maritime sector is reducing emissions, cutting fuel consumption, and complying with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This transition isn’t theoretical—numerous vessels worldwide are already leveraging these groundbreaking technologies to set new standards in efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Featured News

Plugged In but Priced Out? UK Shore Power Faces a Commercial Reality Check

Moscow vs Tehran: Discount Battle Intensifies as China Becomes the Main Prize

Panama Cancels Canal Port Concessions, Hands Temporary Control to Maersk and MSC

China’s Autonomous Feeder Nails First Fully Automated Berthing

The Evolution of Maritime Propulsion Technologies
Electrification and hybrid systems are transforming the maritime industry by integrating battery technologies, advanced energy storage, and renewable energy sources with traditional ship engines. These systems are not limited to theoretical concepts; they are operational in numerous commercial, passenger, and cargo vessels across the globe.
Pioneering Real-World Examples
1. Fully Electric Ships
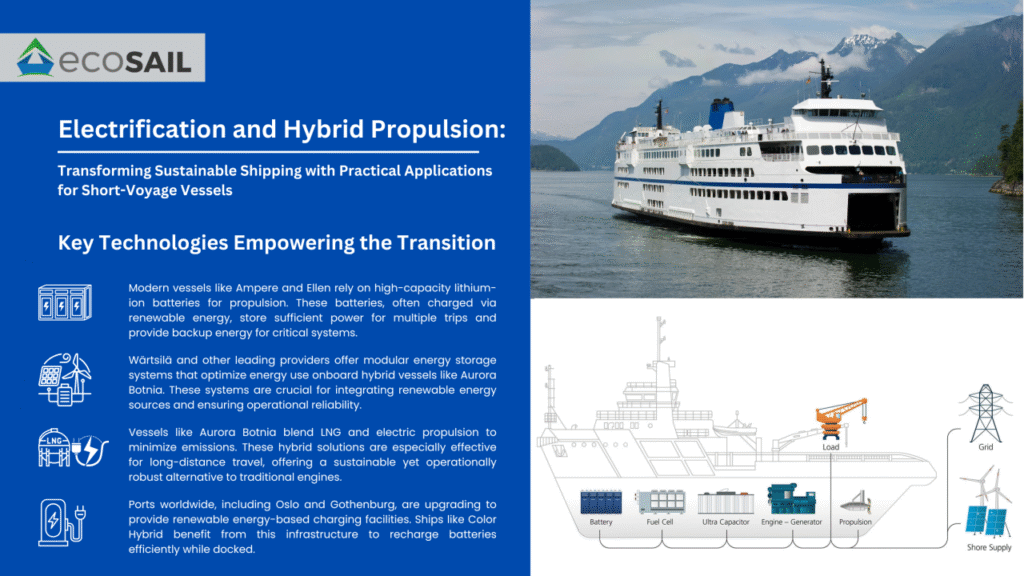
- Ampere (Norway): Operated by Norled, Ampere is the world’s first fully electric car ferry. It utilizes advanced lithium-ion batteries to replace traditional diesel engines, cutting CO2 emissions by up to 95% and eliminating NOx emissions. The ferry operates on a short route between Lavik and Oppedal, recharging its batteries in just 10 minutes.
- Ellen (Denmark): This electric ferry revolutionizes regional transport in Denmark. Powered entirely by batteries, Ellen operates without fossil fuels, enabling zero-emission travel over longer distances than most electric ferries.
2. Hybrid-Electric Vessels
- Color Hybrid (Norway): This hybrid ferry, operated by Color Line, uses battery power during port operations to eliminate local emissions. The ship’s large battery pack charges using renewable energy while docked, reducing its environmental impact even during high-speed cruising.
- Aurora Botnia (Finland): This passenger and cargo ferry employs a hybrid solution combining LNG engines and a battery-powered energy storage system. It operates with up to 50% fewer emissions, thanks to Wärtsilä’s hybrid propulsion technology.
- Stena Jutlandica (Sweden): Operated by Stena Line, this vessel employs a battery-assisted hybrid propulsion system to reduce fuel consumption by 20%, demonstrating the practicality of hybrid systems in larger vessels.

3. Electric Cargo Vessels
- Yara Birkeland (Norway): Known as the world’s first fully autonomous and electric cargo ship, this vessel operates without any crew and entirely on battery power. Designed to eliminate 40,000 truck journeys annually, Yara Birkeland showcases how electrification can revolutionize logistics while reducing CO2 emissions.
- Cargill Kamsarmax: A bulk carrier fitted with a hybrid propulsion system, it combines traditional engines with battery storage to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions during low-speed operations.

4. Renewable Energy Integration
Vindskip (Concept): Designed by Lade AS, this hybrid ship incorporates wind-assisted propulsion to supplement its electric and hybrid systems. Although still a concept, the vessel aims to achieve a 60% reduction in fuel consumption.

Key Technologies Empowering the Transition
1. Advanced Battery Systems Modern vessels like Ampere and Ellen rely on high-capacity lithium-ion batteries for propulsion. These batteries, often charged via renewable energy, store sufficient power for multiple trips and provide backup energy for critical systems.
2. Energy Storage Solutions (ESS) Wärtsilä and other leading providers offer modular energy storage systems that optimize energy use onboard hybrid vessels like Aurora Botnia. These systems are crucial for integrating renewable energy sources and ensuring operational reliability.
3. LNG-Hybrid Systems Vessels like Aurora Botnia blend LNG and electric propulsion to minimize emissions. These hybrid solutions are especially effective for long-distance travel, offering a sustainable yet operationally robust alternative to traditional engines.
4. Shore Power Charging Infrastructure Ports worldwide, including Oslo and Gothenburg, are upgrading to provide renewable energy-based charging facilities. Ships like Color Hybrid benefit from this infrastructure to recharge batteries efficiently while docked
Sustainability and Industry Impact
Environmental Benefits
Fully electric ships like Ellen produce zero emissions, eliminating pollutants such as CO2, NOx, and SOx. Hybrid vessels, although not entirely emission-free, significantly reduce fuel consumption and associated emissions during low-speed and port operations.
Economic Advantages
Reduced reliance on fossil fuels translates to lower operational costs for shipping companies. For instance, Stena Jutlandica has demonstrated fuel savings of 20%, highlighting the cost-efficiency of hybrid systems.
Regulatory Compliance
Technologies such as hybrid propulsion and electrification play a crucial role in helping the shipping industry align with the IMO’s ambitious goal to neutralize greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the potential is immense, challenges like high initial costs, battery energy density, and the need for global charging infrastructure remain significant. However, ongoing advancements in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries, and increased adoption of renewable energy sources offer promising solutions.
Future Outlook: Scaling Sustainability
The success of vessels like Ampere, Yara Birkeland, and Color Hybrid highlights the feasibility and advantages of electrification and hybrid propulsion in shipping. As more companies embrace these technologies, supported by innovations in renewable energy integration and battery advancements, the industry will continue to evolve towards a cleaner, greener future.

